Enhanced analytical and physical characterization of mixtures of random bay-position brominated boron subnaphthalocyanines enabled by establishing a partial separation method†
Abstract
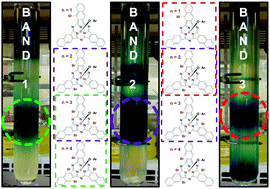
The synthesis of axially brominated boron subnaphthalocyanine (BsubNc) was investigated using BBr3 as the Lewis acid source. Random bay position bromination was found to occur as previously described by our group during the synthesis of chloro-(chloro)n-boron subnaphthalocyanines (Cl-ClnBsubNcs) using BCl3. The direct substitution of BBr3 for BCl3 in the synthesis of BsubNc was found to increase bay position halogenation. We found in this study that it is possible to avoid bay position bromination by employing low temperature synthetic methods. However, these methods were found to yield only analytical amounts of the BsubNc macrocycles, preventing any isolation and physical characterization. We identify herein an appropriate method for scaling of the synthesis of bromo-(bromo)n-boron subnaphthalocyanines (Br-BrnBsubNcs). On the appropriate scaling of the synthesis of bromo-(bromo)n-boron subnaphthalocyanines (Br-BrnBsubNcs), we then conducted axial phenoxylation (ArO-BrnBsubNcs) reactions to enable the separation of the mixture of bay position brominated species by column chromatography. Partial separation was accomplished. Separation and/or purification of Br-BrnBsubNcs is problematic given the known weakness of the B–Br bond which is widely open for hydrolysis. After partial separation, we describe herein analytical methods for the characterization of bay position halogenated BsubNcs with improved resolution and accuracy. These analytical techniques enable the accurate determination of the degrees of bay position halogenation that are present within a mixture of BsubNcs. Quantification of the average bay position halogenation and a description of the halogenated benz(f)isoindoline units within a mixture of bay position BsubNcs is also presented. The photophysical and electrochemical properties of the partially separated ArO-BrnBsubNcs were investigated. Bay position bromination was found to significantly influence these properties. A diminishing influence of bromination as the degree of bromination increased was observed in all cases. Fluorescence quantum yields of ArO-BrnBsubNcs were found to be close to an order of magnitude lower than those of their bay position chlorinated counterparts, presumably due to the heavy atom effect. Solution stability was also investigated, and a degradation product was identified by single-crystal X-ray diffraction analysis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...