Design of carboxylate-based ionic liquids (ILs) containing OH and CF3 groups; influence of intramolecular hydrogen bonds and inductive effect on the binding energy between the cation and anion of ILs, a DFT study†
Abstract
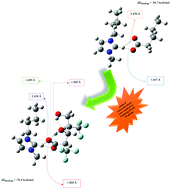
Ionic liquids, which are widely known as room temperature molten salts, have been the subject of much scientific debate for more than a decade. These compounds can be used as green solvents or even as additives in many reactions. Due to their noticeable conductivity, which is a function of the interaction energies existing between the ion pairs in ionic liquids, the synthesis and introduction of new families of these chemicals are of importance. The target of this paper is to design new carboxylate-based ionic liquids containing OH and CF3 groups. Our results indicate that the properties of these ILs are highly affected by the presence of OH and CF3 groups, in which OH stabilizes the negative charge of the anion via intramolecular hydrogen bonds and CF3 stabilizes it through the electron withdrawing effect. These groups decrease the binding energy between the anion and cation of the carboxylate-based ionic liquids and thus affect their physical properties such as melting point and density as well as their chemical properties. All calculations in this study were performed in the gas phase at the B3LYP/6-311++G(d,p) level.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...