Conformational evolution following the sequential molecular dehydrogenation of PMDI on a Cu(111) surface†
Abstract
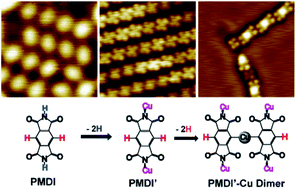
Molecular spatial conformational evolution following the corresponding chemical reaction pathway at surfaces is important to understand and optimize chemical processes. Combining experimental and theoretical methods, the sequential N–H and C–H dehydrogenation of pyromellitic diimide (PMDI) on a Cu(111) surface are reported. STM experiments and atomistic modeling allow structural analysis at each well-defined reaction step. First, exclusively the aromatic N–H dehydrogenation of the imide group is observed. Subsequently, the C–H group at the benzene core of PMDI gets activated leading to a dehydrogenation reaction forming metalorganic species where Cu adatoms pronouncedly protruding from the surface are coordinated by one or two PMDI ligands at the surface. All reactions of PMDI induce conformational changes at the surface as confirmed by STM imaging and DFT simulations. Such conformational evolution in sequential N–H and C–H activation provides a detailed insight to understand molecular dehydrogenation processes at surfaces.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...