Biobased superhydrophobic coating enabled by nanoparticle assembly†
Abstract
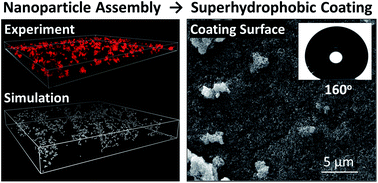
Understanding biobased nanocomposites is critical in fabricating high performing sustainable materials. In this study, fundamental nanoparticle assembly structures at the nanoscale are examined and correlated with the macroscale properties of coatings formulated with these structures. Nanoparticle assembly mechanisms within biobased polymer matrices were probed using in situ liquid-phase atomic force microscopy (AFM) and computational simulation. Furthermore, coatings formulated using these nanoparticle assemblies with biobased polymers were evaluated with regard to the hydrophobicity and adhesion after water immersion. Two biobased glycopolymers, hydroxyethyl cellulose (HEC) and hydroxyethyl starch (HES), were investigated. Their repeating units share the same chemical composition and only differ in monomer conformations (α- and β-anomeric glycosides). Unique fractal structures of silica nanoparticle assemblies were observed with HEC, while compact clusters were observed with HES. Simulation and AFM measurement suggest that strong attraction between silica surfaces in the HEC matrix induces diffusion-limited-aggregation, leading to large-scale, fractal assembly structures. By contrast, weak attraction in HES only produces reaction-limited-aggregation and small compact cluster structures. With high particle loading, the fractal structures in HEC formed a network, which enabled a waterborne formulation of superhydrophobic coating after silane treatment. The silica nanoparticle assembly in HEC was demonstrated to significantly improve adhesion, which showed minimum adhesion loss even after extended water immersion. The superior performance was only observed with HEC, not HES. The results bridge the assembly structures at the nanoscale, influenced by molecular conformation of biobased polymers, to the coating performance at the macroscopic level. Through this study we unveil new opportunities in economical and sustainable development of high-performance biobased materials.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...