Light-activated quantum dot potentiation of antibiotics to treat drug-resistant bacterial biofilms†
Abstract
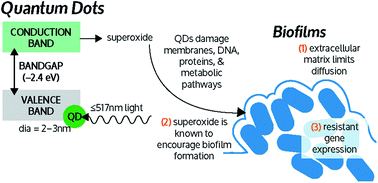
CdTe-2.4 eV quantum dots (QDs) show excellent efficacy due to their tunability and photo-potentiation for sterilizing drug-resistant planktonic cultures without harming mammalian cells but this QD fabrication has not been tested against biofilms. While the QD attack mechanism—production of superoxide radicals—is known to stimulate biofilm formation, here we demonstrate that CdTe-2.4 eV QD-antibiotic combination therapy can nearly eradicate Escherichia coli, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. CdTe-2.4 eV QD versatility, safety, and ability to potentiate antibiotics makes them a potential treatment strategy for biofilm-associated infections.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...