Real-time surface-enhanced Raman scattering-based live cell monitoring of the changes in mitochondrial membrane potential†
Abstract
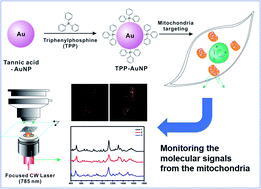
Obtaining molecular information on cells in real time has been a critical challenge in studying the interaction between molecules of interest and intracellular components. Fluorescence-based methods have long served as excellent tools to study such important interactions. In this paper, we introduce a Raman scattering-based method as a promising platform to achieve the real-time monitoring of subtle molecular changes occurring within cells. We found that the Raman scattering-based method enabled monitoring changes in the mitochondrial membrane potential at the single-cell level in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts induced by tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) protein, various chemicals (MgCl2, FCCP, and sodium pyruvate), and a non-chemical stimulus (i.e., light). The triphenylphosphine-modified gold nanoparticles were selectively localized in the mitochondria and showed the characteristic Raman spectrum of cytochrome C and other Raman spectra of molecular components inside the cell. The surface-enhanced Raman spectrum originating from mitochondria was sensitively changed over time when mitochondrial depolarization was induced by the addition of TNF-α, or chemicals known to induce mitochondrial depolarization. The Raman-based signal changes were well matched with results of the conventional fluorescence-based analysis. However, in contrast to the conventional approach, the Raman-based method enables monitoring such changes in real time and provides detailed molecular information in terms of the interaction of molecules. Therefore, these results highlight the possibility of surface-enhanced Raman scattering-based live cell analysis for future proteomics or drug-screening applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...