Fe7Se8 encapsulated in N-doped carbon nanofibers as a stable anode material for sodium ion batteries†
Abstract
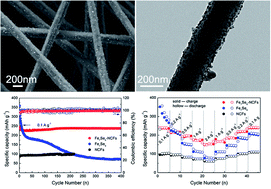
Transition metal chalcogenides especially Fe-based selenides for sodium storage have the advantages of high electric conductivity, low cost, abundant active sites, and high theoretical capacity. Herein, we proposed a facile synthesis of Fe7Se8 embedded in carbon nanofibers (denoted as Fe7Se8-NCFs). The Fe7Se8-NCFs with a 1D electron transfer network can facilitate Na+ transportation to ensure fast reaction kinetics. Moreover, Fe7Se8 encapsulated in carbon nanofibers, Fe7Se8-NCFs, can effectively adapt the volume variation to keep structural integrity during a continuous Na+ insertion and extraction process. As a result, Fe7Se8-NCFs present improved rate performance and remarkable cycling stability for sodium storage. The Fe7Se8-NCFs exhibit practical feasibility with a reasonable specific capacity of 109 mA h g−1 after 200 cycles and a favorable rate capability of 136 mA h g−1 at a high rate of 2 A g−1 when coupled with Na3V2(PO4)3 to assemble full sodium ion batteries.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...