Advances in the electron diffraction characterization of atomic clusters and nanoparticles
Abstract
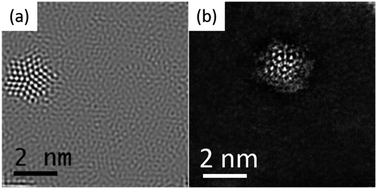
Nanoparticles and metallic clusters continue to make a remarkable impact on novel and emerging technologies. In recent years, there have been impressive advances in the controlled synthesis of clusters and their advanced characterization. One of the most common ways to determine the structures of nanoparticles and clusters is by means of X-ray diffraction methods. However, this requires the clusters to crystallize in a similar way to those used in protein studies, which is not possible in many cases. Novel methods based on electron diffraction have been used to efficiently study individual nanoparticles and clusters and these can overcome the obstacles commonly encountered during X-ray diffraction methods without the need for large crystals. These novel methodologies have improved with advances in electron microscopy instrumentation and electron detection. Here, we review advanced methodologies for characterizing metallic nanoparticles and clusters using a variety of electron diffraction procedures. These include selected area electron diffraction, nanobeam diffraction, coherent electron diffraction, precession electron diffraction, scanning transmission electron microcopy diffraction, and high throughput data analytics, which leverage deep learning to reduce the propensity for data errors and translate nanometer and atomic scale measurements into material data.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Recent Review Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...