Boron-based hybrids as novel scaffolds for the development of drugs with neuroprotective properties†
Abstract
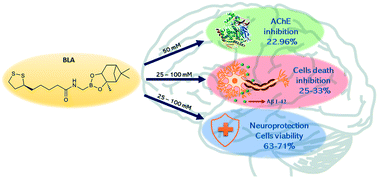
Novel boron-based compounds (BBCs) were synthesized and evaluated as potential candidates for the development of novel drugs against Alzheimer's disease (AD). The neuroprotective profile of novel BBCs was evaluated using Aβ1-42-treated-SH-SY5Y cells while their antioxidant activity was evaluated by total antioxidant capacity (TAC) and total oxidative status (TOS) assays. Results showed that BLA (a novel boron-based hybrid containing an antioxidant portion) inhibited cell death induced by Aβ1-42-exposure in differentiated SH-SY5Y cells, resulting in an increase in cell viability by 25–33% (MTT assay) and by 63–71% (LDH assay) in a concentration range of 25–100 μM. Antioxidant assays demonstrated a good capability of BLA to counteract the oxidative status. Moreover, BLA possessed a significant ability to inhibit acetylcholinesterase (AChE) (22.96% at 50 μM), an enzyme whose enzymatic activity is increased in AD patients. In the present work, absorption and distribution properties of boron-based hybrids were predicted using Pre-ADMET software. In vitro preliminary results suggested that boron-based hybrids could be new structural scaffolds for the development of novel drugs for the management of AD.
- This article is part of the themed collection: NeuroMedChem


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...