Recent developments in sustainable corrosion inhibitors: design, performance and industrial scale applications
Abstract
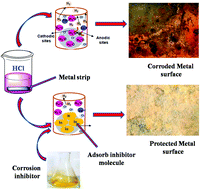
Recently, research studies in the fields of science and engineering are directed towards the synthesis, design, development, and consumption of environment-friendly chemical species to replace traditional toxic chemicals. This is because of the escalating demands of conservation understanding and stringent ecological rules. Currently, various environment-friendly alternatives derived from natural resources such as biopolymers, plant extracts, chemical medicines (drugs), etc. are widely used to replace toxic corrosion inhibitors. Moreover, various biopolymers in their pure and modified forms are extensively employed as environment-friendly corrosion inhibitors. Compounds derived through multicomponent reactions (MCRs), and microwave (MW) and ultrasound (US) irradiations are also considered as environment-friendly alternatives. Polyethylene glycol (PEG) and ionic liquids (ILs) possess low vapor pressure and are regarded as designer environment-friendly alternatives. The chemicals synthesized using green solvents such as water, ILs and supercritical CO2 can also be regarded as environment-friendly chemical species. A comprehensive literature survey reveals that these compounds are extensively utilized as metallic corrosion inhibitors in various corrosive electrolytes. Overall, this review provides a summary of several major reports on environment-friendly corrosion inhibitors.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...