A distance-based capillary biosensor using wettability alteration†
Abstract
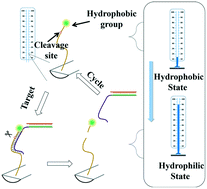
Distance-based detection methods with a quantitative readout are of great significance to point-of-care testing (POCT), are low-cost and user-friendly, and can be integrated into portable analytical devices. Here, we submit a visual quantitative distance-based sensor by capillary force alteration in a capillary tube. This sensor converts the wettability alteration caused by the target molecules into a capillary rise height signal. Moreover, the sensor profits from isothermal amplification technology, achieving the detection of miRNAs with high sensitivity and specificity by visually reading the height of the water in the capillary tube. The proposed biosensor shows great potential in routine clinical diagnosis as well as POCT in resource-limited settings.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...