Highly paralleled emulsion droplets for efficient isolation, amplification, and screening of cancer biomarker binding phages†
Abstract
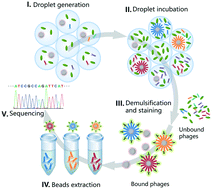
Based on the linkage of genotype and phenotype, display technology has been widely used to generate specific ligands for profiling, imaging, diagnosis and therapy applications. However, due to the lack of effective monoclonal manipulation and affinity evaluation methods, traditional display technology has to undergo tedious steps of selection, clone isolation, amplification, sequencing, synthesis and characterization to obtain the binding sequences. To directly acquire high-affinity clones, we propose a double monoclonal display approach (dm-Display) for peptide screening based on highly paralleled monoclonal manipulation in emulsion droplets. dm-Display can monoclonally link the genotype, phenotype and affinity to realize integrated monoclonal separation, amplification, recognition and staining in one droplet so that discrete high-affinity clones can be quickly extracted. Monoclonal manipulations highly-parallelly occur in millions of droplets so that molecular screening of a highly diverse phage library is achieved. We have screened specific peptide ligands against CD71 and GPC1, proving the feasibility and generality of dm-Display. As a highly efficient ligand screening platform, dm-Display will promote the further development of molecular screening.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...