Investigation of mineral-element migration upon pyrolysis and quantitative prediction of volatiles in coal using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy
Abstract
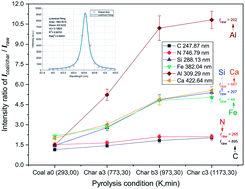
In this study, mineral-element migration upon pyrolysis and quantitative prediction of volatiles were investigated by laser induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) for three characteristic types of coal. KBr was used to polymerize coal or char into a pellet. High percentage of KBr provided a good environment for forming plasmas of stable emissions with relatively high electron excitation temperature and electron density, due to the suppression of the laser-ablation induced pyrolysis of volatile matter. With the increasing pyrolysis temperature, char atomic emissions were greatly increased, which is thought to be related to mineral-element reloading in the char surface upon pyrolysis. Divergence of intensity ratios Ichar/Icoal of Fe/Ca/Mg between high-volatile and low-volatile coal indicates that the Fe/Ca/Mg-containing minerals from volatiles may change their existing forms upon pyrolysis, which can easily trigger more intensive emissions. These findings indicate that LIBS can offer a powerful tool for studying mineral-element migration and contribute to improving numerical simulations of coal pyrolysis and combustion. Finally, multiple linear regression (MLR) and artificial neural network (ANN) methods were applied for quantification of volatile content. MLR models with R2 > 0.977 for single-rank coal samples and ANN models with R2 = 0.991 for all samples were achieved, which provide an accurate and reliable method for industrial coal quality evaluations.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...