Design of a synthetic enzyme cascade for the in vitro fixation of a C1 carbon source to a functional C4 sugar†
Abstract
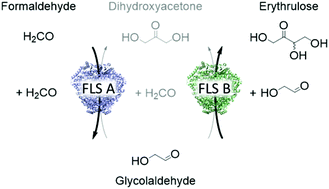
Realizing a sustainable future requires intensifying the waste stream conversion, such as converting the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide into value-added products. In this paper, we focus on utilizing formaldehyde as a C1 carbon source for enzymatic C–C bond formation. Formaldehyde can be sustainably derived from other C1 feedstocks, and in this work, we designed a synthetic enzyme cascade for producing the functional C4 sugar erythrulose. This involved tailoring the enzyme formolase, which was optimized for fusing formaldehyde, from a three-carbon producer (dihydroxyacetone) to sets of variants with enhanced two-carbon (glycolaldehyde) or four-carbon (erythrulose) activity. To achieve this, a high-throughput combinatorial screening was developed, and every single variant was evaluated in terms of glycolaldehyde, dihydroxyacetone and erythrulose activity. By applying the two most promising variants in an enzyme cascade, we were able to show for the first time production of ERY starting from a C1 carbon source. In addition, we demonstrated that one of our tailored formolase variants was able to convert 25.0 g L−1 glycolaldehyde to 24.6 g L−1 erythrulose (98% theoretical yield) in a fully atom-economic biocatalytic process. This represents the highest achieved in vitro concentration of erythrulose to date.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...