Efficient extracellular laccase secretion via bio-designed secretory apparatuses to enhance bacterial utilization of recalcitrant lignin†
Abstract
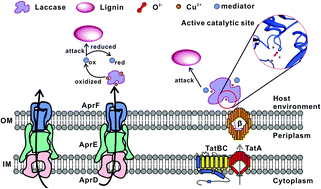
Microbial-driven lignin conversion has a significant impact on the biogeochemistry of global ecosystems and biomass utilization. During this process, secretion of extracellular ligninolytic enzymes is the first, essential step, yet there is a significant challenge to the secretion of these high-redox potential enzymes in bacteria, especially in Gram-negative bacteria. In this study, genome and proteome analyses enabled us to bio-design two types of extracellular secretory apparatus, both of which effectively secreted a heterologous laccase in Pseudomonas putida, up to ∼300 U mL−1. Importantly, a strong cooperation between P. putida A514 cells and the extracellular laccase, which was either released to the medium or displayed on the cell surface, was observed to significantly promote cell growth (9 × 1010 CFUs mL−1) and lignin consumption (12.5%). Chemical analyses of lignin further confirmed the effect on lignin utilization. Moreover, we demonstrated that a free laccase-A514 cell system exhibited greater effect on lignin utilization than that of a cell-immobilized laccase complex, which challenges the current view of bacterial polymer catabolism, and suggests the importance of secretory pathways and sufficient reaction surface for lignin biocatalysis. Our study advances the knowledge of secretion mechanisms in Gram-negative bacteria and provides novel insights into the lignin utilization by extracellular lignolytic enzyme-bacterial cell systems.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...