Isorhamnetin, the xanthine oxidase inhibitor from Sophora japonica, ameliorates uric acid levels and renal function in hyperuricemic mice†
Abstract
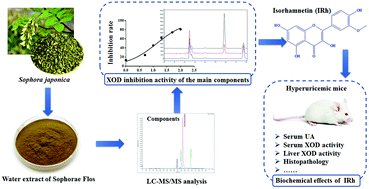
Hyperuricemia is a metabolic condition closely linked to xanthine oxidase (XOD) function, which is involved in the production of uric acid (UA). In this study, XOD was used as a target to construct an in vitro and in vivo activity screening and verification system. The XOD inhibition ability of the main components from the water extract of Sophorae Flos (WSF), an unopened dry flower bud of Sophora japonica, was screened by HPLC. Isorhamnetin (IRh) was identified as a major flavonoid XOD inhibitor from WSF, and we characterized its effects and potential mechanism in ameliorating UA levels and renal function in hyperuricemia model mice. Hyperuricemia was induced by oral administration of potassium oxonate (PO) and hypoxanthine to mice for 7 days. The biochemical index results showed that treatments with low, medium, and high doses of IRh (50, 100, and 150 mg kg−1) significantly reduced serum UA levels and inhibited XOD activity in serum and in the liver. Additionally, IRh effectively decreased the levels of serum creatinine and blood urea nitrogen, suggesting that it possessed nephroprotective effects in hyperuricemic mice. Furthermore, histopathological results showed that nuclear lesions and renal tubule dilatation in the kidneys of IRh-treated hyperuricemic mice were reduced, suggesting that IRh may alleviate renal injury. Molecular docking results showed that IRh combined well with XOD and is an effective XOD inhibitor. In conclusion, IRh from Sophora japonica may reduce the UA levels and alleviate renal injury by inhibiting XOD activity. It potentially functions as a therapeutic drug and dietary supplement to treat hyperuricemia.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...