Pharmacokinetic and excretion study of Aronia melanocarpa anthocyanins bound to amylopectin nanoparticles and their main metabolites using high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry†
Abstract
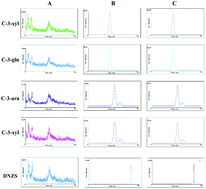
Anthocyanins of Aronia melanocarpa are known for their therapeutic properties; however, they are unstable and easily degrade in the environment and in vivo. Herein, we investigated the stability and bioavailability of four anthocyanins bound to amylopectin nanoparticles (APNPs) through a pharmacokinetic and excretion study using high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. An EC-C18 column with methanol and 0.1% formic acid as the mobile phase was used during the analysis. After APNP treatment, anthocyanins and metabolites exhibited a marked increase, whereas their maximum oral bioavailability reached 440% and 593%, respectively. The delayed elimination half time demonstrated that APNPs had a sustained-release effect on anthocyanins. Pharmacokinetic results revealed that APNPs effectively protect anthocyanins in vivo. Excretion studies in urine and feces had shown a decrease in excretion of anthocyanins and most of the metabolites after APNP treatment. The results of excretion study further proved the protective effect of APNPs on anthocyanins in vivo.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...