Astaxanthin alleviates inflammatory pain by regulating the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and nuclear factor-erythroid factor 2-related factor/heme oxygenase-1 pathways in mice
Abstract
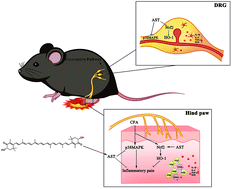
Inflammatory pain is a complex process that has a substantial negative impact on post-injury quality of life. Astaxanthin (AST), which is a lipid-soluble red-orange carotenoid that is found in lobsters, inhibits the development and maintenance of inflammation in mice via its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. However, the specific mechanisms underlying these effects remain unclear. In this study, we aimed to elucidate the mechanism by which astaxanthin alleviated inflammation using a mouse model with Complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA)-induced inflammatory pain. Mechanical allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia were observed on days 1–14 post CFA injection. Expression of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) in the left paw and L4–6 dorsal root ganglia (DRG) were upregulated in the CFA-induced mice. Expression of the nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2)/heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) pathways were also increased. Astaxanthin relieved mechanical allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia induced by CFA and inhibited the inflammatory response (e.g., infiltration of inflammatory cells and production of inflammatory factors) in the ipsilateral paw and DRG. Additionally, AST inhibited p38 MAPK and enhanced Nrf2/HO-1 contents in the left paw and DRG, and reversed the pain induced by p38 MAPK agonist and Nrf2 inhibitors. These findings suggest that AST exerts anti-inflammatory effects and regulates p38 MAPK and Nrf2/HO-1 to alleviate inflammatory pain. AST may be a potential therapeutic agent for relieving inflammation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...