Glucocorticoid receptor-mediated alleviation of inflammation by berberine: in vitro, in silico and in vivo investigations†
Abstract
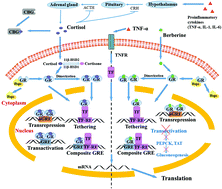
As a natural dietary ingredient, berberine possesses multiple biological activities including anti-inflammatory effects. In this work, glucocorticoid receptor (GR)-mediated alleviation of inflammation by berberine was investigated by a combination of in vitro, in silico, and in vivo approaches. The fluorescence polarization assay showed that berberine bound to GR with an IC50 value of 9.14 ± 0.16 pM. Molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulation suggested that berberine bound stably to the active site of GR via hydrogen bonding and hydrophobic interactions. Berberine induced GR nuclear translocation but did not activate the glucocorticoid response element in HeLa cells. Furthermore, both gene and protein expressions of PEPCK were significantly attenuated by berberine in HepG2 cells. Interestingly, berberine downregulated CBG mRNA and protein levels without up-regulating TAT mRNA and protein levels in HepG2 cells, demonstrating its dissociated characteristics that could separate transrepression from transactivation. In addition, the in vitro and in vivo anti-inflammatory effects of berberine were confirmed in lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW 264.7 cells and in a mouse model of allergic contact dermatitis, respectively. In conclusion, berberine might serve as a potential selective GR modulator.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...