In vitro protein and starch digestion kinetics of individual chickpea cells: from static to more complex in vitro digestion approaches†
Abstract
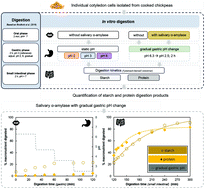
Attention has been given to more (semi-)dynamic in vitro digestion approaches ascertaining the consequences of dynamic in vivo aspects on in vitro digestion kinetics. As these often come with time and economical constraints, evaluating the consequence of stepwise increasing the complexity of static in vitro approaches using easy-to-handle digestion set-ups has been the center of our interest. Starting from the INFOGEST static in vitro protocol, we studied the influence of static gastric pH versus gradual gastric pH change (pH 6.3 to pH 2.5 in 2 h) on macronutrient digestion in individual cotyledon cells derived from chickpeas. Little effect on small intestinal proteolysis was observed comparing the applied digestion conditions. Contrary, the implementation of a gradual gastric pH change, with and without the addition of salivary α-amylase, altered starch digestion kinetics rates, and extents by 25%. The evaluation of starch and protein digestion, being co-embedded in cotyledon cells, did not only confirm but account for the interdependent digestion behavior. The insights generated in this study demonstrate the possibility of using a hypothesis-based approach to introduce dynamic factors to in vitro models while sticking to simple and cost-efficient set-ups.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...