Ursolic acid induces white adipose tissue beiging in high-fat-diet obese male mice
Abstract
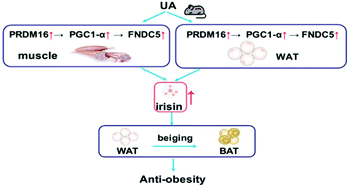
Ursolic acid (UA) shows an effect on obesity and related metabolic diseases, but its mechanism of action remains unclear. We found that UA clearly reduced the body weight and adipose tissue mass and improved the glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity in obese male mice. UA treatment significantly reduced the volume and weights of the epididymal white adipose tissue (eWAT) and inguinal subcutaneous white adipose tissue (igSWAT) of HFD-fed mice, respectively. UA also decreased the expression of genes involved in adipocyte differentiation and lipogenesis in igSWAT. Real-time PCR and immunohistochemistry showed that the expression of beiging-related genes 4-1BB factor (CD137), T-box transcription factor 1 (TBX1), and transmembrane protein 26 (TMEM26) were significantly increased in the UA treatment group. UA treatment significantly reduced the weight of gastrocnemius muscle (GM) and lipid droplets in the GM. UA treatment significantly upregulated the expression of PR domain-containing 16 (PRDM16), peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator-1 alpha (PGC-1α), and fibronectin type 3 domain-containing protein 5 (FNDC5) in GM and igSWAT. UA also stimulated irisin secretion in the serum. In conclusion, these results indicate that UA plays an anti-obesogenic role by increasing the secretion of irisin and promoting the beiging of WAT.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...