Antimicrobial activity, chemical composition and cytotoxicity of Lentinus crinitus basidiocarp
Abstract
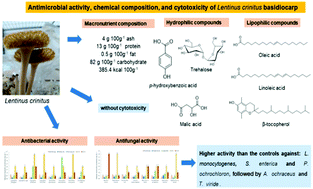
Lentinus crinitus (L.) Fr. (Basidiomycota: Polyporales) is a wild mushroom with several biotechnological applications; however, there are few studies on its chemical composition and antimicrobial activity. Therefore, this study aims to evaluate the chemical composition, cytotoxicity, and antimicrobial activity of L. crinitus basidiocarp. For that, its nutritional value (AOAC procedures) and its composition in some hydrophilic and lipophilic compounds (chromatographic techniques) were assessed. Moreover, the potential hepatotoxic effects were evaluated using a primary cell culture obtained from porcine liver, and its growth inhibitory capacity was also evaluated against four human tumour cell lines (spectrophotometric assays). The antimicrobial activity was evaluated by microdilution against eight bacteria and fungi. The basidiocarp has a high content of carbohydrates and, therefore, a relatively high energetic value. It is also rich in soluble sugars, β-tocopherol, phenolic acids, mainly p-hydroxybenzoic acid, and organic acids, mainly malic acid. L. crinitus did not show cytotoxicity in non-tumour cells, but it did not inhibit the growth of human tumour cell lines either. The basidiocarp has a wide antimicrobial activity, inhibiting the growth of different species of bacteria and fungi. It showed minimum bactericidal and fungicidal concentration values similar to or lower than those verified by commercial antibiotics or food additives used as preservatives. The antimicrobial activity was more evident against Listeria monocytogenes, Salmonella enterica, and Penicillium ochrochloron, followed by Aspergillus ochraceus and Trichoderma viride, when compared to the controls. The results obtained in this study showed that L. crinitus basidiocarp has great potential to be used by the industry without toxicity risks.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...