l-Theanine regulates glutamine metabolism and immune function by binding to cannabinoid receptor 1†
Abstract
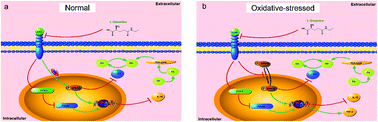
L-Theanine is a characteristic amino acid in tea with various effects including antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. Previously, most studies had reported that L-theanine regulates the immune function in vivo by inhibiting the expression of the inflammatory factors, but how L-theanine regulates the inflammatory factors’ pathway is not known. In this study, we innovatively found the binding target of L-theanine in vivo—cannabinoid receptor 1, and demonstrated that L-theanine regulated the immune function and glutamine metabolism by competitively binding cannabinoid receptor 1. Mechanistically, L-theanine competitively binds cannabinoid receptor 1, leading to inhibition of cannabinoid receptor 1 activity, and regulates glutamine metabolism and immune function in normal and E44813-stressed rats. In normal rats, L-theanine inhibits ERK1/2 phosphorylation through Gβy by antagonizing cannabinoid receptor 1, thus affecting GS expression. From the point of view of immune signaling, after LTA antagonizes the activity of cannabinoid receptor 1, it relieves the inhibition of cannabinoid receptor 1 on COX-2 expression, downregulates Pdcd4 expression and NFκB, and ultimately enhances the expression of the anti-inflammatory factor IL-10. In E44813-stressed rats, L-theanine promotes the nuclear translocation of p-ERK1/2 by inhibiting the activity of cannabinoid receptor 1, and finally acts on GS. At the same time, it decreases the expression of the pro-inflammatory factor TNF-α and increases the expression of the anti-inflammatory factor IL-10 in stressed rats through the COX2-Pdcd4-NFκB-IL10 and TNFα pathways. In summary, these results demonstrate that L-theanine regulates glutamine metabolism and immune function by competitively binding to cannabinoid receptor 1.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...