Polysaccharide MCP extracted from Morchella esculenta reduces atherosclerosis in LDLR-deficient mice
Abstract
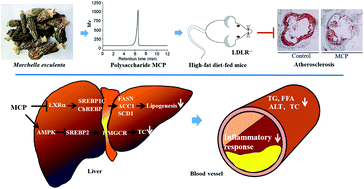
The pharmaceutical application of fungal polysaccharides has been extensively studied based on their multiple biological activities. However, the effect of Morchella esculenta polysaccharides on the development of atherosclerosis remains unknown. This study aims to investigate the anti-atherosclerotic effect of a novel polysaccharide (MCP) extracted from Morchella esculenta. The average molecular weight of MCP is 1.69 × 105 Da, and it is composed of glucose, mannose and galactose in the molar ratio of 1 : 1.9 : 0.51. LDLR-deficient (LDLR−/−) mice were fed high-fat diet (HFD) and administered intragastrically (i.g.) with saline or MCP dissolved in saline for 15 weeks. We found that MCP inhibited en face and sinus lesions. Moreover, serum levels of total and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and triglyceride were decreased by MCP. The HFD-induced hepatic lipid accumulation was also attenuated by MCP. The underlying molecular mechanisms of anti-atherogenic and lipogenic effects of MCP might be attributed to reduced cholesterol synthesis by activating AMPKα signaling pathway and inhibiting SREBP2 expression. In addition, MCP-decreased serum triglyceride level is related to inhibiting LXRα expression. Taken together, these results indicate that MCP markedly alleviates atherosclerosis and M. esculenta can be used as a functional food additive to benefit patients with atherosclerosis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...