The polysaccharides from the Grifola frondosa fruiting body prevent lipopolysaccharide/d-galactosamine-induced acute liver injury via the miR-122-Nrf2/ARE pathways†
Abstract
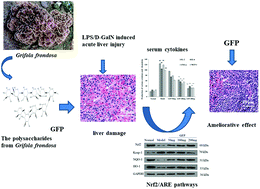
Polysaccharides can be used as a potential hepatoprotective agent in the treatment of acute liver injury. However, the underlying mechanism governing how polysaccharides protect against acute liver injury induced by lipopolysaccharide/D-galactosamine (LPS/D-GalN) remains unclear. To investigate the mechanism, the anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory action and pathways were determined. In this study, we investigated the hepatoprotective effects of Grifola frondosa polysaccharides (GFP), which are obtained from the fruiting body of Grifola frondosa, on (LPS/D-GalN)-induced liver injury in mice. Histopathological analyses showed that GFP protected against LPS/D-GalN-induced lung inflammation. The activities of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and the levels of the inflammatory mediators tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin (IL)-2, IL-6, and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) were inhibited by GFP. The LPS/D-GalN-induced myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity and malondialdehyde (MDA) content were inhibited by GFP. The levels of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione (GSH) were upregulated by GFP. The GFP-treated group showed reduced expression levels of miR-122 in liver tissue. Nrf2 has been identified as a potential target of miR-122. The western blotting results showed that GFP attenuates LPS/D-GalN-induced acute liver injury via upregulating transcription factors Nrf2, Nqo-1, and HO-1 and downregulating transcription factor Keap-1 in the Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway. In conclusion, these results indicated that GFP was highly effective in inhibiting liver injury and may be a promising potential therapeutic reagent for liver injury treatment. GFP exerts protective effects against LPS/D-GalN-induced liver injury in mice, which may be related to the regulation of the miR-122-Nrf2/ARE pathways.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...