Caffeic acid protects against Aβ toxicity and prolongs lifespan in Caenorhabditis elegans models
Abstract
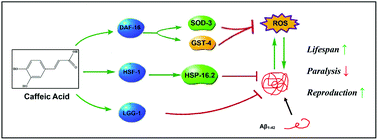
Caffeic acid (CA), a derivative of cinnamic acid, exists in various vegetables and fruits. Natural compounds as beneficial antioxidants play an important role in the research of Alzheimer's disease (AD). In this study, we evaluated the effects of CA against AD using the C. elegans models of AD. We found that CA significantly alleviated Aβ-induced toxicity, increased lifespan, decreased body paralysis, and improved reproductive defects. Also, CA treatment increased resistance to heat and oxidative stress in N2 and CL4176. Moreover, reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels and polyglutamine (polyQ40) aggregate formation were reduced. Furthermore, the mechanistic studies revealed that CA activated transcription factor DAF-16 and its downstream targets SOD-3 and GST-4 to protect against Aβ toxicity. Also, the heat shock proteins hsf-1 and hsp-16.2 mRNA were up-regulated in CL4176. Moreover, CA activated the mRNA expression of lgg-1. Lastly, the KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) analysis of RNA-seq data revealed that there was a significant change in the metabolism-related pathways. Overall, these results suggested an underlying mechanism of action of CA in treating AD at an organism level.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...