Diosmetin attenuates metabolic syndrome and left ventricular alterations via the suppression of angiotensin II/AT1 receptor/gp91phox/p-NF-κB protein expression in high-fat diet fed rats
Abstract
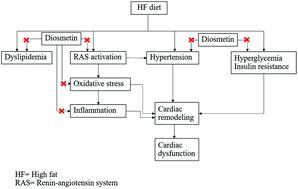
Diosmetin, a monomethoxyflavone, is isolated from citrus fruits. The objective of this research was to test the biological role of diosmetin on parameters of metabolic syndrome (MS) and left ventricular (LV) alterations in rats fed with a high-fat (HF) diet. MS was induced by feeding male Sprague-Dawley rats with a HF diet plus 15% fructose in drinking water for 16 weeks. MS rats were given diosmetin (20 or 40 mg per kg per day) or metformin (100 mg per kg per day) for the final four weeks. Diosmetin attenuated signs of MS including, hypertension, hyperglycemia, insulin resistance, and dyslipidemia in rats that received the HF diet (p < 0.05). A decreased stroke volume, ejection fraction, fractional shortening, LV hypertrophy and fibrosis present in the MS group were alleviated by diosmetin treatment (p < 0.05). Diosmetin also suppressed angiotensin-converting enzyme activity, plasma angiotensin II (Ang II) levels and angiotensin II type 1 (AT1) receptor protein expression in MS rats. Increases in superoxide (O2˙−) formation, plasma malondialdehyde, plasma nitrate and nitrite and gp91phox expression induced by a HF diet were ameliorated in the diosmetin treated group. Inflammation indicated by an increased phospho nuclear factor kappa B (p-NF-κB) protein expression and cardiac TNF-α concentration was reduced in MS rats receiving diosmetin (p < 0.05). Metformin also attenuated MS, cardiac abnormalities relevant to decreasing the renin–angiotensin system stimulation, reactive oxygen species and inflammation in MS rats (p < 0.05). Diosmetin alleviated MS and LV dysfunction and remodeling in HF diet-induced MS rats. These results could be associated with the suppression of the Ang II/AT1 receptor/gp91phox/p-NF-κB protein pathway.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...