Effect of konjac glucomannan on metabolites in the stomach, small intestine and large intestine of constipated mice and prediction of the KEGG pathway
Abstract
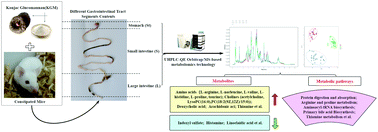
The occurrence of constipation involves the whole gastrointestinal tract. Konjac glucomannan (KGM) has been clinically proven to alleviate constipation, but its mechanism has not been fully understood. The present study aimed to investigate the excretion-promoting effect of KGM on constipated mice and the underlying molecular mechanism. In this study, the UHPLC-QE orbitrap/MS method was used to determine the metabolic phenotypes of total gastrointestinal segments (i.e., the stomach {St}, small intestine {S}, and large intestine {L}) in constipated mice treated with KGM. The results showed that KGM improved the fecal water content, body weight growth rate, and serum gastrointestinal regulation related peptide levels. The metabolomics results revealed the decreased levels of amino acids, cholines, deoxycholic acid, arachidonic acid, thiamine and the increased levels of indoxyl sulfate, histamine, linoelaidic acid etc. The KEGG pathway analysis indicated that the relaxation effect of KGM supplementation was most likely driven by modulating the expression levels of various key factors involved in biosynthesis of amino acid (i.e., phenylalanine, tyrosine and tryptophan), linoleic acid metabolism, biosynthesis of secondary metabolites, and arachidonic acid metabolism signalling pathways. The results indicated that KGM alleviates constipation by regulating potential metabolite markers and metabolic pathways in different gastrointestinal segments.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...