Investigation into effects of warmer conditions on seasonal runoff and dissolved carbon fluxes in permafrost catchments in northeast China
Abstract
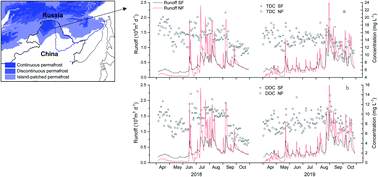
Eurasian permafrost serves as an important carbon pool and water resource for linked aquatic ecosystems. To investigate the effects of expected warmer climate under climate change, and also to fill the data gaps in the south margin of the Eurasian permafrost, the seasonal runoff and the associated dissolved carbon fluxes in a pair of catchments in the Great Khingan Mountains of northeast China were investigated in 2018–2019. Two similar small catchments, a south-facing (SF) and a north-facing (NF), were used to check the effects of warmer climate on the dynamics of runoff and dissolved carbon yields. The SF catchment, with a warmer condition compared to the NF catchment, presented much larger snowmelt runoff during spring and more gentle rainfall flood peaks in the summer–autumn period, but similar concentrations of dissolved carbons during both the periods. As a result, the dissolved carbon fluxes were greatly elevated during the snowmelt period. However, the runoff and carbon yield in the two catchments showed no significant difference during the summer rainfall periods, in spite of a much deeper active layer of permafrost in the SF. As indicated by two fluorescence indices, the humification (HIX) and biological index (BIX), the chemical characteristics of dissolved carbon were similar in both the snowmelt and rainfall runoff periods in the two catchments. These results emphasize that warmer climate would largely alter the seasonal runoff patterns and promote dissolved carbon export in the snowmelt period, which would lead to more unexpected ecological impacts on the aquatic systems in the south Eurasian permafrost.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...