Discriminatory behavior of a rhodamine 6G decorated mesoporous silica based multiple cation sensor towards Cu2+ and Hg2+vis-à-vis Al3+, Cr3+ and Fe3+: selective removal of Cu2+ and Hg2+ from aqueous media†
Abstract
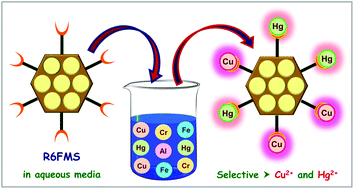
Selective identification of metal ions as well as their removal is possible when a sensing unit is anchored to a solid support. In this paper, functionalized mesoporous silica with a pendant rhodamine 6G moiety (R6FMS) has been obtained by successive grafting of an aldehyde derivative of bisphenol A followed by rhodamine 6G over a 3-aminopropyl anchored mesoporous silica framework. The materials have been characterized by powder X-ray diffraction, nitrogen sorption and electron microscopy studies, FT-IR and solid state MAS NMR spectral studies, and thermal analysis. In ethanol, the colorless silica material gives pink coloration in the presence of Al3+, Cr3+, Fe3+ and Cu2+ which is also clearly evident from the generation of an absorption peak at 525 nm. Upon excitation at 500 nm, the fluorescence intensity of the probe increases by 36-, 17-, 40- and 89-fold in the presence of Al3+, Cr3+, Fe3+ and Cu2+ ions, respectively. This suggests that R6FMS is a colorimetric and fluorescent chemosensor for these cations in ethanol. However, when the solvent is changed from ethanol to water, it becomes a selective chemosensor only for Cu2+ and Hg2+, by the generation of a pink color and strong fluorescence at ca. 550 nm, thereby discriminating the trivalent cations. Cations induce the opening of the spirolactam ring resulting in pink coloration and strong fluorescence. The quantum yield and lifetime of the probe have been increased considerably in the presence of these cations in ethanol as well as in aqueous media. The detection limit values for these cations range from 10−6 to 10−8 M. R6FMS has been used to remove Hg2+ and Cu2+ from their aqueous solution with a maximum adsorption capacity of 35 mg g−1 and 148 mg g−1 for Cu2+ and Hg2+, respectively.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...