Fluorescent palladium(ii) and platinum(ii) NHC/1,2,3-triazole complexes: antiproliferative activity and selectivity against cancer cells†
Abstract
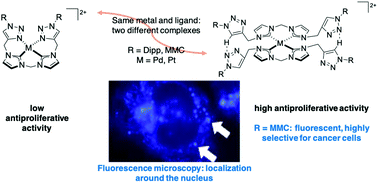
Fluorescent Pd(II) and Pt(II) complexes bearing 4-methylene-7-methoxycoumarin (MMC) and 2,6-diispropylphenyl (Dipp) substituted NHC/1,2,3-triazole hybrid ligands are described. Depending on the reaction conditions two different ligand coordination modes are observed, i.e., bidentate solely coordinating via NHCs or tetradentate coordinating via NHCs and 1,2,3-triazoles. All Dipp substituted complexes show antiproliferative activity against cervix (HeLa) and breast (MCF-7) human carcinoma cells. The activity significantly depends on the coordination mode, with the tetradentate motif being notably more effective (HeLa: IC50 = 3.9 μM to 4.7 μM; MCF-7: IC50 = 2.07 μM to 2.35 μM). Amongst the MMC series, only the Pd(II) complex featuring the bidentate coordination mode is active against HeLa (IC50 = 6.1 μM). In contrast to its structurally related Dipp derivative (SI = 0.6), it shows a high selectivity for HeLa (SI > 16) compared to healthy skin cells (HaCaT). According to fluorescence microscopy, this compound is presumably located in late endosomes or lysosomes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...