Synthetic ferripyrophyllite: preparation, characterization and catalytic application†
Abstract
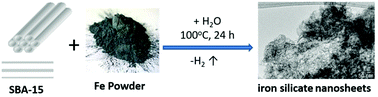
Sheet silicates, also known as phyllosilicates, contain parallel sheets of tetrahedral silicate built up by [Si2O5]2− entities connected through intermediate metal–oxygen octahedral layers. The well-known minerals talc and pyrophyllite are belonging to this group based on magnesium and aluminium, respectively. Surprisingly, the ferric analogue rarely occurs in nature and is found in mixtures and conglomerates with other materials only. While partial incorporation of iron into pyrophyllites has been achieved, no synthetic protocol for purely iron-based pyrophyllite has been published yet. Here we report about the first artificial synthesis of ferripyrophyllite under exceptional mild conditions. A similar ultrathin two-dimensional (2D) nanosheet morphology is obtained as in talc or pyrophyllite but with iron(III) as a central metal. The high surface material exhibits a remarkably high thermostability. It shows some catalytic activity in ammonia synthesis and can serve as catalyst support material for noble metal nanoparticles.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...