Al-Modified Ti-MOR as a robust catalyst for cyclohexanone ammoximation with enhanced anti-corrosion performance†
Abstract
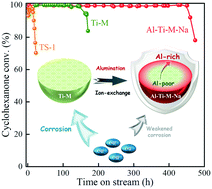
The skeleton desilication accompanied by Ti active sites leaching accounts for the dominant chemical deactivation reasons during the clean industrial production of cyclohexanone oxime through titanosilicate-catalyzed liquid-phase ammoximation in the alkali reaction system. In this study, aluminum species were reintroduced into Ti-MOR by hydrothermal post-treatment with aluminum salts to enhance its anti-corrosion performance against alkaline medium and catalytic stability in cyclohexanone ammoximation reaction. The undesired strengthening in hydroxylamine decomposition and oxime hydrolysis derived from the implantation of aluminum into the framework could be eliminated via further Na+-exchange. By means of quenching bridging Si(OH)Al-related acidic sites selectively, the exchanged process then enhanced catalytic activity significantly in both the hydroxylamine formation and ammoximation processes. With aluminum species enriched on the crystal shell, Ti-MOR after aluminated and Na+-exchanged (denoted as Al-Ti-M-Na) showed a more robust performance in the simulated desilication process and a tremendously prolonged ammoximation lifetime of 460 h, which was 2.75 times that of pristine Ti-MOR. The unprecedented duration of Al-Ti-M-Na was mainly ascribed to the protective effect of the Al-rich shell as it served as the guardian crust that defended the Ti active sites against leaching caused by desilication and skeleton destruction.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...