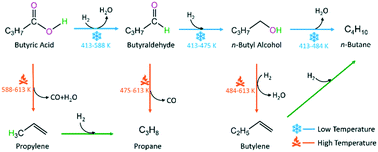
For the deoxygenation of fatty acids to hydrocarbon biofuels, the catalytic mechanism is still unclear at the molecular level. Here, the deoxygenation mechanism of butyric acid catalyzed by a Ni12P6 cluster has been theoretically studied at the GGA–PBE/DNP, DSPP level in dodecane solution, in which butyric acid and the Ni12P6 cluster are preferred as the reactant model of palmitic acid and the catalyst model of Ni2P, respectively. For the deoxygenation of butyric acid, there are three main reactions i.e., (reaction (I)) through direct decarboxylation to propane, (reaction (II)) through decarbonylation and hydrodehydration/hydroreduction to propane, and (reaction (III)) through hydroreduction and/or hydrodehydration to n-butane. Propane stems from the decarbonylation (reaction (II)) rather than direct decarboxylation (reaction (I)). For reaction (II), the optimal pathway should be through butyraldehyde or direct decarbonylation and not through propyl alcohol. Furthermore, CO mainly originates from butyraldehyde at low temperature and from direct decarbonylation at high temperature. From butyraldehyde, decreasing temperature is beneficial to the n-butyl alcohol formation through hydroreduction, and increasing temperature is preferable to the propane formation through decarbonylation. For reaction (III), from n-butyl alcohol, n-butane comes from direct hydrodehydration at low temperature, and from successive dehydration and hydroreduction through n-butylene at high temperature. The present reaction mechanism network may promote the novel design of a highly selective catalyst toward the deoxygenation of fatty acids.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...