The cooperative role of innocent ligand in N-heterocyclic carbene manganese catalyzed carbon dioxide hydrogenation†
Abstract
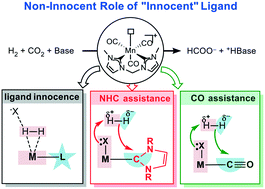
N-Heterocyclic carbene (NHC) and carbonyl (CO) ligands are generally regarded as innocent ligands in bifunctional catalysts. However, their non-innocent roles in cooperation as Lewis acid sites due to their π-accepting characteristics have long been neglected. Herein, the unprecedented cooperation roles of NHC and CO ligands were systematically investigated for N-heterocyclic carbene manganese complex promoted CO2 hydrogenation to formate by density functional theory (DFT) studies. Our results demonstrate the important cooperation role of the CO ligand, which could assist the reaction by stabilizing the negatively charged hydride. Two energetically accessible and competitive mechanisms are located, including the innocent ligand mechanism with activation free energy of 29.4 kcal mol−1 and the non-innocent CO-assisted mechanism with activation free energy of 27.2 kcal mol−1. In contrast, the NHC-assisted mechanism has a higher free energy barrier (34.1 kcal mol−1) for H2 heterolysis compared to the CO-assisted case, which should be mainly attributed to the more acidic π* orbital of the CO ligand than that of the NHC ligand. The possibility of the involvement of CO ligand as a Lewis acid was verified by the relevant reported crystal structures in the literature. The unfolded significant cooperation role of the CO ligand, which is generally neglected in conventional studies, should provide important mechanistic insights into the rational design of bifunctional catalysts with conventional innocent ligands.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...