Exceptionally stable sol-immobilization derived Pd/SBA-15 catalysts for methane combustion†
Abstract
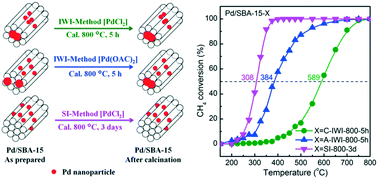
Pd-Based catalysts are efficient for methane combustion but impractical at high temperatures due to the sintering effect. Herein, we report a thermally stable Pd/SBA-15 catalyst that was prepared by using the sol-immobilization (SI) method, instead of the conventional incipient wetness impregnation (IWI) method. Pd nanoparticles retain the small size of ∼5 nm in the channels of SBA-15 in Pd/SBA-15-SI even after aging at 800 °C in air for 3 days, while those in the Pd/SBA-15-IWI samples aggregate into particles larger than 10 nm over the surface. The thermally stable Pd/SBA-15-SI indeed displays excellent catalytic activity for methane combustion at low temperatures with T50 at ∼300 °C and T90 at ∼350 °C and high stability during cyclic operations, which are much superior to those of the Pd/SBA-15-IWI catalysts. Interestingly, hydrothermal treatment of the Pd/SBA-15-SI catalysts leads to partial re-dispersion of Pd to form smaller particles of ∼1.6 nm, while the catalytic activity decreases a bit. Steam in the reactant mixture has a negative effect on the catalytic activity of Pd/SBA-15-SI catalysts, presumably due to the competitive adsorption of H2O to O2/CH4. Significantly, the size of Pd nanoparticles is essential to the catalytic performance and those having sizes of ∼5 nm are the most active. Finally, the catalytic activity of the catalysts in the presence of CO2 was studied. This work might be helpful in designing stable metal catalysts using porous materials for reactions under harsh conditions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...