Continuous enzymatic stirred tank reactor cascade with unconventional medium yielding high concentrations of (S)-2-hydroxyphenyl propanone and its derivatives†
Abstract
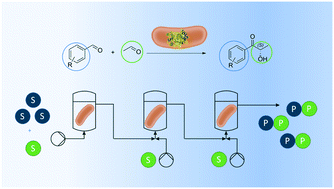
The implementation of biocatalysis in flow chemistry offers synergistic synthesis advantages in line with green chemistry principles. Yet, the conversion of high substrate concentrations is in many cases hindered by insolubility issues or substrate toxicity. Here, the continuous synthesis of (S)-2-hydroxyphenyl propanone (2-HPP) from inexpensive benzaldehyde and acetaldehyde in a methyl tert-butyl ether based organic reaction environment, namely micro-aqueous reaction system, has been established. Kinetic parameters of the applied whole cell catalyst were identified to design a continuous process for (S)-2-HPP synthesis. This revealed a necessity to distribute acetaldehyde over a spatial coordinate to remain below a toxic concentration threshold. Hence, three continuous stirred tank reactors (cSTR) were conjugated in a technical cascade with an additional influx of acetaldehyde into each unit. The catalytic behaviour of this reaction setup was described based on mass balances and a kinetic model. Enzyme deactivation was described by a novel staged model and compared to a simple generic model. The optimized continuous setup yielded 190 mM (S)-HPP with an ee > 98% over 8 h. The product was easily recovered from the organic reaction environment by crystallization with an isolated yield of 68% and a purity of >99%. Further, the substrate range of the applied catalyst Pseudomonas putida benzoylformate decarboxylase variant L461A was analysed. This revealed numerous halogenated, methoxylated and nitro-derivatives in ortho, meta, and para position, which can in principle be gained by the established process. As an example, the applied cSTR concept was transferred to p-methoxy benzaldehyde with good results even without further optimization.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Biocatalysis: A cross-journal collection


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...