Towards the development of the emerging process of CO2 heterogenous hydrogenation into high-value unsaturated heavy hydrocarbons
Abstract
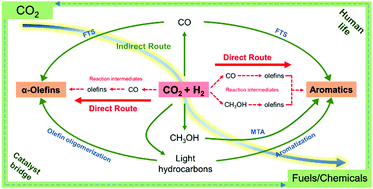
The emerging process of CO2 hydrogenation through heterogenous catalysis into important bulk chemicals provides an alternative strategy for sustainable and low-cost production of valuable chemicals, and brings an important chance for mitigating CO2 emissions. Direct synthesis of the family of unsaturated heavy hydrocarbons such as α-olefins and aromatics via CO2 hydrogenation is more attractive and challenging than the production of short-chain products to modern society, suffering from the difficult control between C–O activation and C–C coupling towards long-chain hydrocarbons. In the past several years, rapid progress has been achieved in the development of efficient catalysts for the process and understanding of their catalytic mechanisms. In this review, we provide a comprehensive, authoritative and critical overview of the substantial progress in the synthesis of α-olefins and aromatics from CO2 hydrogenation via direct and indirect routes. The rational fabrication and design of catalysts, proximity effects of multi-active sites, stability and deactivation of catalysts, reaction mechanisms and reactor design are systematically discussed. Finally, current challenges and potential applications in the development of advanced catalysts, as well as opportunities of next-generation CO2 hydrogenation techniques for carbon neutrality in future are proposed.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...