Advances in multiplexed techniques for the detection and quantification of microRNAs
Abstract
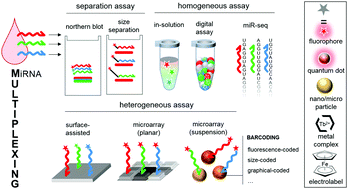
MicroRNA detection is currently a crucial analytical chemistry challenge: almost 2000 papers were referenced in PubMed in 2018 and 2019 for the keywords “miRNA detection method”. MicroRNAs are potential biomarkers for multiple diseases including cancers, neurodegenerative and cardiovascular diseases. Since miRNAs are stably released in bodily fluids, they are of prime interest for the development of non-invasive diagnosis methods, such as liquid biopsies. Their detection is however challenging, as high levels of sensitivity, specificity and robustness are required. The analysis also needs to be quantitative, since the aim is to detect miRNA concentration changes. Moreover, a high multiplexing capability is also of crucial importance, since the clinical potential of miRNAs probably lays in our ability to perform parallel mapping of multiple miRNA concentrations and recognize typical disease signature from this profile. A plethora of biochemical innovative detection methods have been reported recently and some of them provide new solutions to the problem of sensitive multiplex detection. In this review, we propose to analyze in particular the new developments in multiplexed approaches to miRNA detection. The main aspects of these methods (including sensitivity and specificity) will be analyzed, with a particular focus on the demonstrated multiplexing capability and potential of each of these methods.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...