Surface chemistry at the solid–solid interface: mechanically induced reaction pathways of C8 carboxylic acid monolayers on copper
Abstract
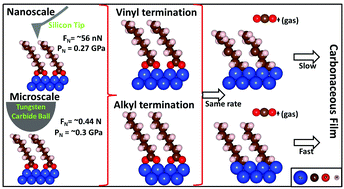
Mechano- or tribochemical processes are often induced by the large pressures, of the order of 1 GPa, exerted at contacting asperities at the solid–solid interface. These tribochemical process are not very well understood because of the difficulties of probing surface-chemical reaction pathways occurring at buried interfaces. Here, strategies for following surface reaction pathways in detail are illustrated for the tribochemical decomposition of 7-octenoic and octanoic acid adsorbed on copper. The chemistry was measured in ultrahigh vacuum by sliding either a tungsten carbide ball or a silicon atomic force microscope (AFM) tip over the surface to test a previous proposal that the nature of the terminal group in the carboxylic acid, vinyl versus alkyl, could influence its binding to the counterface, and therefore the reaction rate. The carboxylic acids bind strongly to the copper substrate as carboxylates to expose the hydrocarbon terminus. The tribochemical reaction rate was found to be independent of the nature of the hydrocarbon terminus, although the pull-off and friction forces measured by the AFM were different. The tribochemical reaction is initiated in the same way as the thermal reaction, by the carboxylate group tilting to eliminate carbon dioxide and deposit alkyl species onto the surface. This reaction occurs thermally at ∼640 K, but tribochemically at room temperature, producing significant differences in the rates and selectivities of the subsequent decomposition pathways of the adsorbed products.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2021 PCCP HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...