Fabrication and application of composite adsorbents made by one-pot electrochemical exfoliation of graphite in surfactant ionic liquid/nanocellulose mixtures†
Abstract
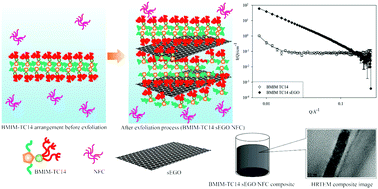
Previously, surfactant-assisted exfoliated graphene oxide (sEGO) formed with the triple-chain surfactant TC14 (sodium 1,4-bis(neopentyloxy)-3-(neopentylcarbonyl)-1,4-dioxobutane-2-sulfonate) was applied in wastewater treatment. The extent of dye-removal and the adsorption capacity of the sEGO formed with this triple-chain surfactant outperformed those of two other systems, namely, the di-chain version of TC14 (AOT14; sodium 1,2-bis-(2,2-dimethyl-propoxycarbonyl)-ethanesulfonate) and the single-chain surfactant sodium n-dodecylsulfate. In the present study, to further optimise the surfactant chemical structure, the sodium ion of TC14 was substituted with 1-butyl-3-methyl-imidazolium (BMIM) generating surfactant ionic liquids (SAILs; 1-butyl-3-imidazolium 1,4-bis(neopentyloxy)-3-(neopentyloxycarbonyl)-1,4-dioxobutane-2-sulfonate), hereafter denoted as BMIM-TC14. This SAIL, together with nanofibrillated kenaf cellulose (NFC), was used to electrochemically exfoliate graphite, yielding BMIM-TC14 sEGO/NFC composites. These highly hydrophobic polymer composites were then used for the removal of methylene blue (MB) from aqueous solution. 1H NMR spectroscopy was used to elucidate the structure of the synthesised SAILs. The morphologies of the resulting nanocomposites were investigated using Raman spectroscopy, field-emission scanning electron microscopy, and high-resolution transmission electron microscopy. Analysis using small-angle neutron scattering was performed to examine the aggregation behaviour of sEGO and custom-made SAILs. Zeta potential, surface tension, and dynamic light-scattering measurements were used to study the aqueous properties and colloidal stability of the suspension. Amongst the surfactants tested, BMIM-TC14 sEGO/NFC exhibited the highest MB adsorption ability, achieving 99% dye removal under optimum conditions. These results highlight the importance of modifying the hydrophilic moieties of amphiphilic compounds to improve the performance of sEGO/NFC composites as effective adsorbents for wastewater treatment.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2021 PCCP HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...