A combined experimental and theoretical study of miconazole salts and cocrystals: crystal structures, DFT computations, formation thermodynamics and solubility improvement†
Abstract
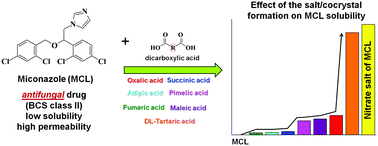
Experimental and theoretical screening of multi-component crystal forms of miconazole (MCL), an antifungal drug, with ten aliphatic dicarboxylic acids was performed. Seven multi-component molecular crystals were isolated and identified by different analytical techniques, including the powder X-ray diffractometry (PXRD), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), thermogravimetric analysis (TG), and solubility methods. The crystal structures of the MCL hemihydrate, two cocrystals with succinic ([MCL + SucAc] (2 : 1)) and fumaric acids ([MCL + FumAc] (2 : 1)) and one salt with maleic acid ([MCL + MleAc] (1 : 1)) were redetermined. The new cocrystal of MCL with adipic acid ([MCL + AdpAc] (2 : 1)) was investigated by single crystal X-ray diffractometry. It was found that the AdpAc molecule in the cocrystal has an unusual anticlinal conformation. The combination of periodic density functional theory (DFT) computations and quantum topology analysis confirmed the structure-directing role of the acid-imidazole heterosynthon for the considered crystals. The melting temperatures of all the studied multi-component crystals are between the values of the corresponding individual components except [MCL + MleAc] (1 : 1). A thermal analysis has shown that the thermodynamic and thermophysical characteristics of the considered two-component molecular crystals are strongly dependent both on specific interactions (presence of sites of donor–acceptor interactions and hydrogen bond formation) and on nonspecific interactions – molecule polarizability. Based on the sublimation thermodynamics database of molecular crystals, the standard sublimation thermodynamic functions of MCL were evaluated. The thermodynamic functions of multi-component crystal formation based on MCL were calculated and analyzed. Solubility experiments on the MCL multi-component crystals were carried out in isotonic aqueous buffer solutions at pH 1.2 and 6.8 and compared with the solubility of the MCL free base and its nitrate salt. It was found that the salt/cocrystal formation of MCL with dicarboxylic acids considerably increased the MCL solubility in pH 6.8 buffer. The biggest MCL solubility enhancement was observed in the [MCL + TartAc] (1 : 1) salt. The solubility value of MCL in the [MCL + TartAc] (1 : 1) salt is commensurate with the commercial MCL nitrate salt.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...