High coordination number actinide-noble gas complexes; a computational study†
Abstract
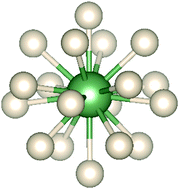
The geometries, electronic structures and bonding of early actinide-noble gas complexes are studied computationally by density functional and wavefunction theory methods, and by ab initio molecular dynamics. AcHe183+ is confirmed as being an 18-coordinate system, with all of the He atoms accommodated in the primary coordination shell, and this record coordination number is reported for the first time for Th4+ and Th3+. For Pa and U in their group valences of 5 and 6 respectively, the largest number of coordinated He atoms is 17. For AnHe17q+ (An = Ac, q = 3; An = Th, q = 4; An = Pa, q = 5; An = U, q = 6), the average An–He binding energy increases significantly across the series, and correlates linearly with the extent of He → Anq+ charge transfer. The interatomic exchange–correlation term Vxc obtained from the interacting quantum atoms approach correlates linearly with the An–He quantum theory of atoms-in-molecules delocalization index, both indicating that covalency increases from AcHe173+ to UHe176+. The correlation energy in AnHe163+ obtained from MP2 calculations decreases in the order Pa > Th > U > Ac, the same trend found in Vxc. The most stable complexes of Ac3+ with the heavier noble gases Ar–Xe are 12 coordinate, best described as Ng12 cages encapsulating an Ac3+ ion. There is enhanced Ng → Ac3+ charge transfer as the Ng gets heavier, and Ac–Ng covalency increases.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...