A density functional theory study on the underwater adhesion of catechol onto a graphite surface†
Abstract
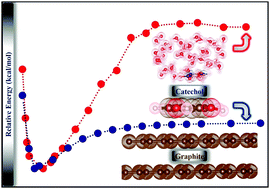
Mussel foot proteins (MFPs) strongly adhere to both hydrophilic and hydrophobic surfaces under wet conditions. This water-resistant adhesion of MFP is ascribed to catechol (1,2-dihydroxybenzene) which is highly contained in the MFP. Currently, little is known about the molecular details of the underwater adhesion of catechol onto a nonpolar hydrophobic surface. By using the density functional theory, we investigate the adhesion of catechol onto a wet graphite surface. We unveil the molecular geometry and energy in the course of the wet adhesion of catechol. Catechol adheres through π–π stacking with the underlying graphite. The surrounding water molecules further strengthen the adhesion by forming hydrogen bonds with catechol. In addition, a significant charge transfer has been observed from wet graphite to the catechol. Consequently, catechol adheres onto the present hydrophobic surface as strongly as onto a hydrophilic silica surface.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...