Structural and dynamic properties of some aqueous salt solutions†
Abstract
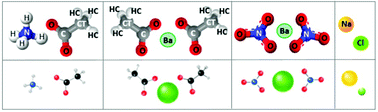
Aqueous salt solutions are utilized and encountered in wide-ranging technological applications and natural settings. Towards improved understanding of the effect of salts on the dynamic properties of such systems, dilute aqueous salt solutions (up to 1 molar concentration) are investigated here, via experiments and molecular simulations. Four salts are considered: sodium chloride, for which published results are readily available for comparison, ammonium acetate, barium acetate and barium nitrate, for which published data are scarce. In the present work, molecular dynamics (MD) simulations are conducted to quantify viscosity and water self-diffusion coefficients, together with rheometry and Pulsed Field Gradient Spin Echo (PFGSE)-NMR experiments for validation. Simulation predictions are consistent with experimental observations in terms of trend and magnitude of salt-specific effects. Combining insights from the approaches considered, an interpretation of the results is proposed whereby the capacity of salts to influence bulk dynamics arises from their molecular interfacial area and strength of interaction with first hydration-shell water molecules. For the concentration range investigated, the interpretation could be useful in formulating aqueous systems for applications including the manufacturing of advanced catalysts.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...