Understanding the interlayer rearrangement toward enhanced lithium storage for LiBC anodes†
Abstract
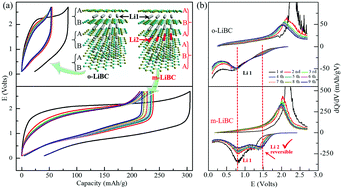
By introducing Li insufficiency, we interestingly found that m-LiBC exhibits a higher capacity (220 mA h g−1) than the original o-LiBC (50 mA h g−1). This improved capacity benefits from its structural evolution, with the interlayer rearrangement changed from “ABABAB” (o-LiBC) to “ABAABA” (m-LiBC) stacking, triggered by Li insufficiency. This understanding of interlayer rearrangement for LiBC may open a new avenue to activate Li+ extraction in other lithium compounds.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...