Deep learning-driven scaffold hopping in the discovery of Akt kinase inhibitors†
Abstract
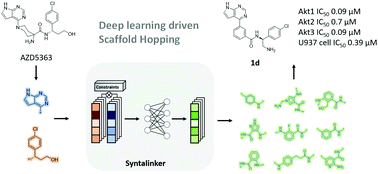
Scaffold hopping has been widely used in drug discovery and is a topic of high interest. Here a deep conditional transformer neural network, SyntaLinker, was applied for the scaffold hopping of a phase III clinical Akt inhibitor, AZD5363. A number of novel scaffolds were generated and compound 1a as a proof-of-concept was synthesized and validated by biochemical assay. Further structure-based optimization of 1a led to a novel Akt inhibitor with high potency (Akt1 IC50 = 88 nM) and in vitro antitumor activities.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...