Anionic redox reaction triggered by trivalent Al3+ in P3-Na0.65Mn0.5Al0.5O2†
Abstract
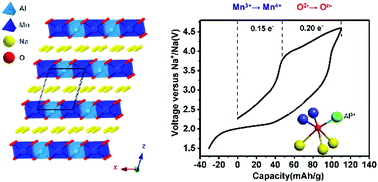
P3-Na0.65Mn0.5Al0.5O2 (NMAO) has been synthesized and studied as a cathode for sodium batteries, and shows anionic redox reaction (ARR) and exhibits a first charging capacity of ∼110 mA h g−1. The electrochemical mechanism of NMAO was comprehensively investigated by X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), Raman spectroscopy, and density functional theory (DFT) calculations. The reversible oxygen redox behaviour is triggered by Al3+ through oxygen quasi non-bonding states generated by the relatively ionic interaction of Al and O. Furthermore, the presence of Al3+ can suppress oxygen loss in ARR. This work provides new insights into the design and mechanism of anionic redox active cathode materials.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Chemical Communications HOT articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...