Red to near-infrared phosphorescent Ir(iii) complexes with electron-rich chelating ligands
Abstract
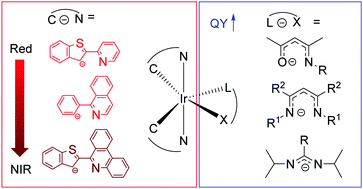
The design of molecular phosphors with near-unity photoluminescence quantum yields in the low-energy regions of the spectrum, red to near-infrared, is a long-standing challenge. Because of the energy gap law and the quantum mechanical dependence of radiative decay rate on the excited-state energy, compounds which luminesce in this region of the spectrum typically suffer from low quantum yields. In this article, we highlight our group's advances in the design of top-performing cyclometalated iridium complexes which phosphoresce in red to near-infrared regions. The compounds we have introduced in this body of work have the general formula Ir(C^N)2(L^X), where C^N is a cyclometalating ligand that controls the photoluminescence color and L^X is a monoanionic chelating ancillary ligand. The Ir(C^N)2(L^X) structure type is among the most widely studied and technologically successful classes of molecular phosphors, particularly when L^X = acetylacetonate (acac). In our work we have pioneered the use of electron-rich, nitrogen containing ancillary (L^X) ligands as a means of controlling the excited-state dynamics and optimizing them to give record-breaking phosphorescence quantum yields. This paper progresses through our work in three distinct regions of the spectrum – red, deep-red, and near-infrared – and summarizes the many insights we have gained on the relationships between molecular structure, frontier orbital energies, and excited-state dynamics.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...