Long-term cycling stability of NiCo2S4 hollow nanowires supported on biomass-derived ultrathin N-doped carbon 3D networks as an anode for lithium-ion batteries†
Abstract
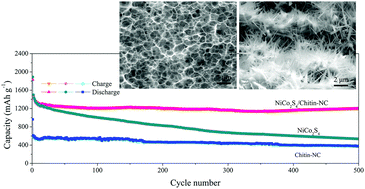
A bio-based N-doped carbon 3D network is designed to fabricate a composite anode for LIBs. Benefiting from the highly active substrate and the supported NiCo2S4 hollow nanowires, the composites exhibit an ultrahigh reversible capacity of 1198 mA h g−1 after 500 cycles, holding great potential for long-term applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...